Hydroelectric power: it sounds so clean, so renewable, almost too good to be true. But before we all jump on the hydro bandwagon, let's take a moment to consider the other side of the coin. While the promise of harnessing the power of water is alluring, there are definitely downsides that deserve our attention.
Many believe hydroelectricity is a perfect solution to our energy needs, a guilt-free source of power. However, dismissing the potential challenges can lead to overlooking critical environmental and social impacts, hindering truly sustainable energy development. Ignoring these issues can result in poorly planned projects that do more harm than good in the long run.
This post dives deep into the disadvantages of hydroelectric power. We'll explore the environmental, social, and economic costs associated with dams and reservoirs. From habitat destruction and displacement of communities to greenhouse gas emissions and high initial costs, we'll uncover the less talked about aspects of this seemingly "green" energy source.
While hydroelectric power offers renewable energy, it's crucial to acknowledge the significant environmental consequences like habitat destruction, altered river ecosystems, and potential methane emissions. Social impacts include displacement of communities and disruption of traditional livelihoods. Economically, the high initial construction costs and long-term maintenance pose considerable challenges. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for informed energy policy and the pursuit of genuinely sustainable solutions.
Environmental Impact: A Delicate Balance Disturbed
The term "environmental impact" seems broad, but when it comes to hydroelectric power, it manifests in very specific and often devastating ways. I remember visiting a national park a few years ago, renowned for its pristine river system. The ranger explained how a proposed dam upstream would drastically alter the river's flow, impacting the delicate ecosystem that supported unique fish species and riparian habitats. It brought home the harsh reality of how these projects, while intended to generate clean energy, can irrevocably alter the natural world.
Dams fundamentally change river ecosystems. They block fish migration routes, preventing species like salmon from reaching their spawning grounds. This can lead to population declines and even extinctions. Reservoirs inundate vast areas of land, destroying forests, wetlands, and other vital habitats. The altered flow regimes downstream can also negatively impact water quality, sediment transport, and the overall health of the river. Furthermore, the decomposition of organic matter in reservoirs can release significant amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to climate change. The environmental consequences are multifaceted and far-reaching, requiring careful consideration before embarking on such projects.
High Initial Costs and Construction Time
Building a hydroelectric dam is not a small undertaking; it's a massive engineering feat with a price tag to match. The initial costs are staggering, encompassing everything from site surveys and environmental impact assessments to the actual construction of the dam and power plant. These projects often require significant government investment or private funding, making them economically challenging to implement.
Beyond the monetary costs, the construction time is another significant factor. Building a large hydroelectric dam can take years, even decades, to complete. This prolonged construction period can delay the benefits of the project and create uncertainty for communities affected by the development. The long lead times also mean that the project may be subject to changing energy policies and economic conditions, potentially impacting its viability. Moreover, cost overruns are common in large infrastructure projects, further exacerbating the economic challenges associated with hydroelectric power.
Displacement of Communities and Cultural Heritage
Perhaps one of the most heart-wrenching disadvantages of hydroelectric power is the displacement of communities. When a dam is built, the reservoir that forms behind it often inundates entire villages, forcing people to leave their homes, lands, and ancestral territories. This displacement can have devastating social, economic, and cultural consequences.
Relocating communities is a complex and often traumatic process. People lose their livelihoods, their social networks, and their connection to their cultural heritage. Resettlement programs are often inadequate, failing to provide displaced communities with the resources and support they need to rebuild their lives. Furthermore, the loss of cultural heritage sites, such as sacred places and archaeological sites, can have a profound impact on the identity and well-being of affected communities. The displacement of communities is a serious ethical concern that must be carefully considered before any hydroelectric project is undertaken.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Surprising Contributor?
It's often surprising to hear that hydroelectric power can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, given its reputation as a clean energy source. However, reservoirs can actually release significant amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas that is far more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide. This methane is produced by the decomposition of organic matter in the flooded areas.
The amount of methane emitted from reservoirs can vary depending on factors such as the size of the reservoir, the amount of organic matter present, and the water temperature. In some cases, reservoirs can emit more greenhouse gases than traditional fossil fuel power plants. This is particularly true in tropical regions where warmer temperatures promote faster decomposition rates. While hydroelectric power is still generally considered to be a lower-carbon energy source than fossil fuels, it's important to acknowledge the potential for greenhouse gas emissions from reservoirs and to take steps to minimize these emissions.
Recommendation: Comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessments
To mitigate the negative impacts of hydroelectric power, it's crucial to conduct thorough and comprehensive environmental impact assessments before any project is undertaken. These assessments should consider all potential environmental, social, and economic consequences, including the impacts on water quality, fish populations, terrestrial habitats, greenhouse gas emissions, and local communities.
The assessment process should be transparent and inclusive, involving stakeholders from all affected groups, including local communities, environmental organizations, and government agencies. The results of the assessment should be used to inform the design and implementation of the project, ensuring that mitigation measures are in place to minimize negative impacts. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and evaluation should be conducted throughout the life of the project to assess the effectiveness of the mitigation measures and to identify any unforeseen consequences. By taking a proactive and comprehensive approach to environmental impact assessment, we can minimize the risks associated with hydroelectric power and ensure that it contributes to a truly sustainable energy future.
The Importance of Community Consultation
Community consultation is an absolutely vital component of any hydroelectric project, or really any large-scale infrastructure project that impacts local populations. Too often, decisions are made behind closed doors, with little or no input from the people who will be directly affected by the development. This can lead to resentment, distrust, and ultimately, project failure. Genuine community consultation means engaging with local communities early in the planning process, providing them with accurate and accessible information about the project, and listening to their concerns and suggestions. It means being willing to adapt the project design to address those concerns, and ensuring that communities benefit from the project in a tangible way, whether through employment opportunities, improved infrastructure, or access to electricity. It's about recognizing that communities have valuable knowledge and expertise, and that their participation is essential for creating a project that is both economically viable and socially responsible.
Tips for Minimizing the Disadvantages
While the disadvantages of hydroelectric power are significant, there are steps that can be taken to minimize these impacts. First and foremost, it's crucial to prioritize smaller, run-of-river projects that have a lower environmental footprint than large dams. These projects typically do not require large reservoirs and have less impact on river ecosystems.
Another important tip is to invest in fish passage technologies, such as fish ladders and elevators, to allow fish to migrate freely past dams. These technologies can help to mitigate the impact of dams on fish populations and maintain the health of river ecosystems. Furthermore, it's important to implement measures to minimize greenhouse gas emissions from reservoirs, such as removing vegetation before flooding and managing water levels to reduce methane production. By adopting these strategies, we can reduce the negative impacts of hydroelectric power and make it a more sustainable energy source.
Exploring Alternative Energy Sources
While hydroelectric power has its place in the energy mix, it's essential to explore and invest in alternative renewable energy sources that have a lower environmental impact. Solar power, wind power, geothermal energy, and biomass are all promising alternatives that can help us to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and create a more sustainable energy future. Each of these sources has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the optimal mix of energy sources will vary depending on local conditions and resources. However, by diversifying our energy portfolio and investing in innovative technologies, we can create a more resilient and sustainable energy system that meets our needs without compromising the health of the planet.
Fun Facts About Hydroelectric Power
Did you know that the world's first hydroelectric power plant was built in Northumberland, England in 1878? It was used to power a single arc lamp at a country house. This early example of hydroelectric power demonstrates the long history of harnessing water for electricity generation.
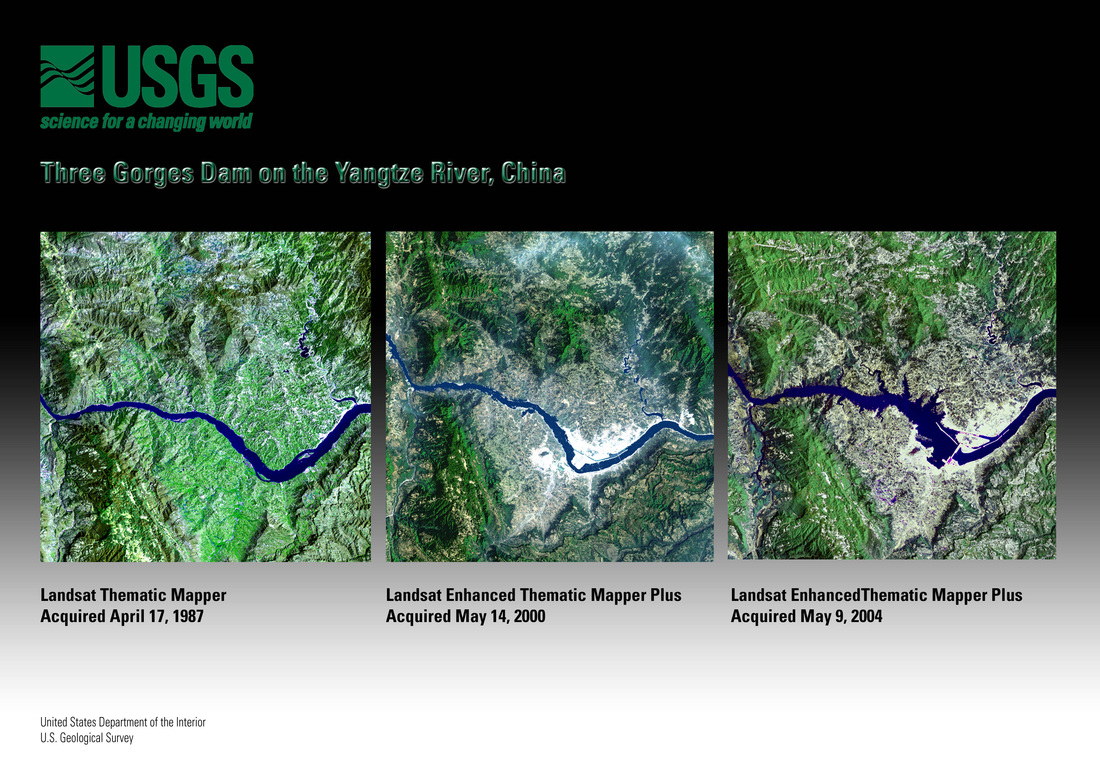
Another fun fact is that the Three Gorges Dam in China is the world's largest hydroelectric power plant. It has a generating capacity of over 22,500 megawatts, which is enough to power millions of homes. However, the Three Gorges Dam has also been controversial due to its significant environmental and social impacts. Despite the drawbacks of hydroelectric power, it remains a significant source of renewable energy worldwide, providing electricity to millions of people and contributing to efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
How to Mitigate the Negative Impacts
Mitigating the negative impacts of hydroelectric power requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the environmental and social consequences of these projects. This includes implementing best practices for dam design and construction, such as minimizing the size of reservoirs, preserving riparian habitats, and installing fish passage facilities. It also requires engaging with local communities and ensuring that they are adequately compensated for any losses they may experience as a result of the project.
Furthermore, it's important to conduct ongoing monitoring and evaluation to assess the effectiveness of mitigation measures and to identify any unforeseen consequences. Adaptive management strategies should be implemented to adjust the project as needed to minimize negative impacts and maximize benefits. By taking a proactive and comprehensive approach to mitigation, we can reduce the negative impacts of hydroelectric power and ensure that it contributes to a more sustainable energy future.
What If We Ignore the Disadvantages?
Ignoring the disadvantages of hydroelectric power can have serious and far-reaching consequences. If we fail to adequately assess and mitigate the environmental impacts, we risk causing irreversible damage to river ecosystems, leading to the extinction of fish species, the loss of biodiversity, and the degradation of water quality. If we fail to engage with local communities and address their concerns, we risk causing social unrest, displacement, and the erosion of cultural heritage. If we fail to consider the economic costs and risks associated with hydroelectric projects, we risk wasting valuable resources and creating unsustainable development.
Moreover, if we continue to rely on hydroelectric power without exploring alternative renewable energy sources, we risk becoming overly dependent on a single energy source and vulnerable to fluctuations in water availability due to climate change. It's therefore essential to take a holistic and responsible approach to energy planning, considering all of the potential consequences of our choices and prioritizing solutions that are both environmentally sustainable and socially just.
Listicle: Key Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power
Here's a quick list to summarize the main drawbacks:
- Environmental Impact: Habitat destruction, altered river ecosystems, methane emissions.
- High Initial Costs: Expensive construction and long lead times.
- Community Displacement: Loss of homes, livelihoods, and cultural heritage.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Reservoirs can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Dependence on Water Availability: Vulnerable to droughts and climate change.
Being aware of these downsides allows for more informed decision-making when considering hydroelectric power as an energy solution.
Question and Answer
Q: Is hydroelectric power really a "clean" energy source?
A: While it doesn't directly emit pollutants like fossil fuels, the creation and operation of hydroelectric dams can have significant environmental impacts, including methane emissions from reservoirs and habitat destruction.
Q: Why are the initial costs of hydroelectric projects so high?
A: The construction of dams and power plants is a massive undertaking, requiring extensive engineering, materials, and labor. Environmental impact assessments and mitigation measures also add to the overall cost.
Q: What happens to the communities that are displaced by hydroelectric projects?
A: Displacement can lead to the loss of homes, livelihoods, and cultural heritage. While resettlement programs are often offered, they may not adequately compensate for the losses experienced by affected communities.
Q: Can the negative impacts of hydroelectric power be mitigated?
A: Yes, through careful planning, comprehensive environmental impact assessments, community engagement, and the implementation of best practices for dam design and operation, negative impacts can be minimized.
Conclusion of Top Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power You Should Know
Hydroelectric power, while a renewable energy source, presents a complex web of disadvantages that demand careful consideration. From the far-reaching environmental consequences and the displacement of communities to the substantial financial investments and potential greenhouse gas emissions, understanding these drawbacks is crucial for making informed decisions about our energy future. By acknowledging these challenges and actively seeking mitigation strategies, we can strive for a more balanced and sustainable approach to energy production.