Ever wondered how a river's flow can light up our homes? It's not magic, but a fascinating feat of engineering! Hydroelectric power stations, those often-imposing structures nestled beside rivers and dams, harness the power of water to create electricity. It's a renewable energy source that's been around for over a century, and it's playing an increasingly important role in our quest for a sustainable future.
Understanding the intricacies of power generation can sometimes feel like navigating a complex maze. The technical jargon, the intricate systems, and the sheer scale of these operations can be overwhelming, especially for those just starting to explore the world of renewable energy. It's easy to get lost in the details and feel like you're missing the bigger picture.
This article aims to demystify hydroelectric power stations, providing a beginner-friendly guide to understanding how they work, the different types that exist, and their significance in the broader energy landscape. We'll break down the core concepts in a clear and concise manner, so you can grasp the fundamentals and appreciate the ingenuity behind this clean energy technology. This includes the basic components of a hydroelectric power station, different types of hydroelectric power plants, benefits and challenges, future trends, and frequently asked questions.
We've explored the basics of hydroelectric power stations, from the fundamental principles of harnessing water's energy to the various types of plants and their associated benefits and challenges. By understanding these concepts, you're equipped to appreciate the role of hydropower in our energy future. Hydropower, renewable energy, electricity generation, turbines, dams, and sustainability are keywords to remember on this topic.
The Basic Components of a Hydroelectric Power Station
My first encounter with a hydroelectric power station was during a family trip to the Hoover Dam. I remember being awestruck by the sheer size and scale of the dam. The guide explained how the water rushing through the turbines generated electricity for millions of homes. That's when it clicked for me – it wasn't just a big wall of concrete, but a complex system working in harmony with nature. It sparked my curiosity to understand the individual components that made it all possible.
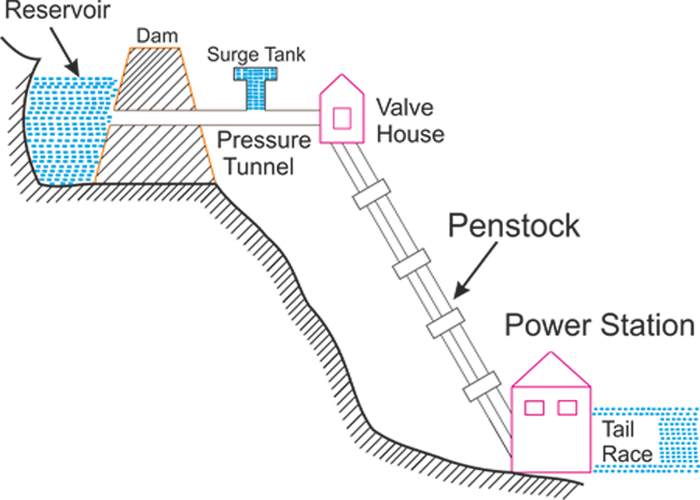
A hydroelectric power station, at its core, relies on a few key components working together: the dam, the reservoir, the penstock, the turbine, the generator, and the transformer. The dam creates a reservoir, storing a large volume of water at a higher elevation. The penstock is a channel or pipe that directs the water from the reservoir to the turbine. The turbine, resembling a giant fan, is spun by the force of the water, converting the water's kinetic energy into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then used to rotate the generator, which converts it into electrical energy. Finally, the transformer increases the voltage of the electricity so it can be efficiently transmitted over long distances via power lines.
Understanding these basic components is crucial for grasping the overall process. The dam acts as the initial energy storage device, while the turbine and generator are the heart of the electricity production. The penstock acts as the channel that controls and directs the flow of water. Each component plays a crucial role in converting the potential energy of water into usable electricity. Variations in design and size exist depending on the location and scale of the power station.
Different Types of Hydroelectric Power Plants
Hydroelectric power plants aren't all created equal. They come in various forms, each suited to different geographical conditions and energy needs. The most common types are impoundment facilities, pumped storage facilities, and run-of-river facilities. Impoundment facilities, like the Hoover Dam, are the most familiar. They use a dam to create a large reservoir, storing water for later use. Pumped storage facilities are like energy batteries, using excess electricity to pump water uphill to a reservoir, and then releasing it back down to generate power during peak demand. Run-of-river facilities, on the other hand, divert a portion of a river's flow through a channel or penstock to spin turbines, with minimal storage capacity. These types of hydroelectric power plants differ on storage, output, and impact on river ecosystems.
The choice of which type of power plant to build depends on several factors, including the availability of a suitable dam site, the water flow characteristics of the river, and the electricity demand patterns of the region. Impoundment facilities offer the greatest control over water flow and power generation, but they also have the largest environmental impact. Run-of-river facilities have a smaller environmental footprint, but their power output is more dependent on the natural flow of the river.
Pumped storage facilities, while requiring significant initial investment, provide valuable grid stability by storing excess energy and releasing it when needed. They can play a critical role in integrating intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the electricity grid. As the demand for clean energy grows, pumped storage is becoming an increasingly attractive option for balancing supply and demand.
History and Myth of Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
The history of hydroelectric power is intertwined with human ingenuity and the quest for harnessing natural resources. While large-scale hydroelectric power stations are a relatively modern invention, the basic principle of using water to power machines dates back centuries. Ancient civilizations used waterwheels to grind grain and perform other mechanical tasks. The first hydroelectric power plant was built in 1878 in Northumberland, England, using a water turbine to power a single lamp.
One common misconception is that hydroelectric power is always "clean" and environmentally friendly. While it is a renewable energy source with no direct emissions during operation, the construction of large dams can have significant environmental impacts, including altering river ecosystems, displacing communities, and affecting fish migration. It's important to consider these impacts when evaluating the overall sustainability of hydroelectric power projects. It's a balance of energy generation and ecological preservation.
Another myth is that hydroelectric power is only suitable for large rivers and mountainous regions. While these locations are ideal, smaller-scale hydroelectric projects can be developed on smaller streams and rivers, providing a distributed source of renewable energy for local communities. Advancements in turbine technology are making it possible to harness the power of even low-head waterways. It is about adapting to the environment and available resources to sustainably leverage hydropower.
Hidden Secrets of Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
Beyond the basic components and types of power plants, there are a few less-known aspects of hydroelectric power that are worth exploring. One is the use of fish ladders and other fish passage technologies to mitigate the impact of dams on fish populations. These structures allow fish to bypass the dam and continue their upstream migration, helping to maintain healthy fish populations.
Another secret is the potential for hydroelectric power plants to provide ancillary services to the electricity grid, such as frequency regulation and voltage support. These services are crucial for maintaining the stability and reliability of the grid, especially as the penetration of intermittent renewable energy sources increases. Hydroelectric power plants can respond quickly to changes in demand, helping to keep the grid in balance.
Finally, the design and operation of hydroelectric power plants are constantly evolving, with advancements in turbine technology, dam safety, and environmental mitigation. Researchers are exploring new materials, designs, and operating strategies to improve the efficiency and sustainability of hydroelectric power. There is always room for improvement and innovation in this field, ensuring it remains a viable source of energy.
Recommendation of Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
If you're interested in learning more about hydroelectric power, I recommend starting with reputable sources such as the International Hydropower Association (IHA) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). These organizations provide a wealth of information on the technology, economics, and environmental aspects of hydroelectric power. There are also numerous books, articles, and documentaries available that can provide a deeper understanding.
Visiting a hydroelectric power station is a great way to see the technology in action and learn firsthand how it works. Many power stations offer tours to the public, providing a unique opportunity to observe the turbines, generators, and other equipment up close. The experience will certainly give you a new appreciation for the complexities and benefits of generating power through hydro.
Consider engaging with experts in the field. Many universities and research institutions have hydroelectric power programs where you can get involved in research projects or take courses. Attending conferences and workshops is also a great way to network with professionals and learn about the latest developments in the industry. It's about building a network and being a part of the renewable energy future.
Environmental Impact of Hydroelectric Power
While hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source, it's important to acknowledge its potential environmental impacts. The construction of dams can alter river ecosystems, affecting fish migration, water quality, and sediment transport. Reservoirs can also inundate land, displacing communities and impacting wildlife habitats. It is crucial to weigh the environmental impacts when comparing to other sources of energy generation.
However, hydroelectric power can also have environmental benefits. Reservoirs can provide water for irrigation, flood control, and recreation. Hydroelectric power plants do not produce air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Many modern hydroelectric projects incorporate environmental mitigation measures, such as fish ladders and minimum flow requirements, to minimize their impact on the environment. These techniques help lessen the impact on local ecosystems by providing more natural environments.
The key to sustainable hydroelectric power is careful planning and management. This includes conducting thorough environmental impact assessments, involving local communities in the decision-making process, and implementing appropriate mitigation measures. By considering both the benefits and the impacts, we can ensure that hydroelectric power plays a positive role in our energy future. Hydroelectric power is an important renewable energy that needs to be considered with all possible environmental mitigations.
Tips of Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
For those just starting to learn about hydroelectric power, here are a few tips to keep in mind. First, focus on understanding the basic principles of how hydroelectric power plants work. Don't get bogged down in the technical details right away. Once you have a solid foundation, you can then delve deeper into the specific components and technologies. Look at diagrams and videos to better understand the basic principles.
Second, explore the different types of hydroelectric power plants and their respective advantages and disadvantages. This will help you understand the factors that influence the choice of which type of power plant to build in a given location. Learning about each type will show the benefits of all types of power plants.
Finally, stay informed about the latest developments in hydroelectric power technology and policy. The industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and regulations emerging all the time. By staying up-to-date, you can ensure that you have a comprehensive understanding of the role of hydroelectric power in the future energy landscape. Keeping up to date helps understand the landscape of new technology and policy.
Future Trends in Hydroelectric Power
The future of hydroelectric power is likely to be characterized by increased emphasis on sustainability, efficiency, and grid integration. Advancements in turbine technology are making it possible to generate more power with less water, reducing the environmental impact of hydroelectric power plants. Modern turbines allow for improved power generation.
Smart grid technologies are enabling hydroelectric power plants to play a more active role in balancing the electricity grid, providing ancillary services and integrating intermittent renewable energy sources. Technologies also enable better balancing of energy and power generation.
There is also growing interest in developing new hydroelectric projects in developing countries, where access to electricity is limited. However, it's important to ensure that these projects are developed in a sustainable manner, with careful consideration of environmental and social impacts. This will help to reduce the number of areas with limited access to electricity. The advancement of hydroelectric power will aid in sustainable energy generation.
Fun Facts of Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
Did you know that the world's largest hydroelectric power plant is the Three Gorges Dam in China? It has a generating capacity of over 22,500 megawatts, enough to power millions of homes. It's a massive engineering achievement with significant energy output. The power plant is a modern marvel of engineering.
Another fun fact is that some hydroelectric power plants are located underground. These plants are typically built in mountainous regions, where the water is diverted through tunnels to underground turbines. Underground plants make it easier to take advantage of mountain water flow.
Hydroelectric power is also used to power electric trains and trams. The electricity generated by hydroelectric power plants can be used to electrify transportation systems, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. In this way, hydroelectric power plants help reduce emissions from transporation fuels. Hydroelectric power is a critical element in moving away from fossil fuels.
How to Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
To get started with hydroelectric power basics, first understand the water cycle and how potential energy is stored in water at higher elevations. Then, study the basic components of a hydroelectric power plant, such as the dam, turbine, generator, and transformer, to visualize the process. Comprehending this process will make the system easier to understand.
Next, investigate the different types of hydroelectric power plants, including impoundment, pumped storage, and run-of-river facilities. Each type has unique characteristics and applications, so it's crucial to grasp the variations. Knowing the distinctions between power plant types is important.
Finally, stay informed on the latest advancements and challenges in the hydroelectric power industry. Explore renewable energy websites, industry publications, and educational resources. Continuous learning is key to staying current with the innovations in the sector. Keeping up to date on renewable energy helps with knowing the innovations of the section.
What If Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
What if we fully embraced hydroelectric power as a primary energy source? The potential benefits are enormous. We could significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, and create a more sustainable energy future. The benefits of less reliance on fossil fuels would lead to decreased emissions and greenhouse gases.
However, the transition to a fully hydroelectric-powered world would not be without challenges. The construction of new dams could have significant environmental impacts, and existing dams would need to be managed carefully to ensure environmental sustainability. These challenges would need careful planning and management.
Furthermore, the distribution of hydroelectric resources is uneven, with some regions having abundant water resources and others facing scarcity. This would require innovative solutions for energy storage and transmission to ensure that everyone has access to affordable and reliable electricity. However, proper planning would enable more reliable electricity for everyone.
Listicle of Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
Here's a quick listicle to summarize the key points about hydroelectric power station basics:
- Hydroelectric power harnesses the energy of moving water to generate electricity.
- Key components include a dam, reservoir, turbine, generator, and transformer.
- Different types of hydroelectric power plants exist, including impoundment, pumped storage, and run-of-river facilities.
- Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source with no direct emissions during operation.
- Construction of dams can have environmental impacts, which must be carefully managed.
- Hydroelectric power can provide ancillary services to the electricity grid, such as frequency regulation.
- Advancements in turbine technology are improving the efficiency and sustainability of hydroelectric power.
- The future of hydroelectric power is likely to be characterized by increased emphasis on sustainability and grid integration.
Question and Answer
Here are some frequently asked questions about hydroelectric power:
Q: Is hydroelectric power really renewable?
A: Yes, hydroelectric power is considered a renewable energy source because it uses the natural water cycle to generate electricity. As long as there is rainfall, the water will replenish, and the power station can continue to generate electricity.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of hydroelectric power?
A: The construction of dams can alter river ecosystems, affecting fish migration, water quality, and sediment transport. Reservoirs can also inundate land, displacing communities and impacting wildlife habitats.
Q: How efficient is hydroelectric power?
A: Hydroelectric power is one of the most efficient forms of electricity generation, with efficiencies typically ranging from 80% to 90%. This means that a large percentage of the water's energy is converted into electricity.
Q: Can hydroelectric power be used in developing countries?
A: Yes, hydroelectric power can be a valuable source of electricity in developing countries, especially those with abundant water resources. However, it's important to ensure that these projects are developed in a sustainable manner, with careful consideration of environmental and social impacts.
Conclusion of Hydro Electric Power Station Basics for Beginners
Hydroelectric power is a crucial part of our energy mix, offering a renewable and efficient way to generate electricity. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and a commitment to sustainability promise a brighter future for this time-tested technology. By understanding the basics, you can better appreciate the role hydroelectric power plays in powering our world and contributing to a cleaner energy future.